What Is The Emerging Impact Of Blockchain And Cryptocurrency In The Financial Services Industry?
Blockchain is transforming everything from payments transactions to how coin is raised in the private market. Volition the traditional banking industry embrace this technology or exist replaced by it?
Blockchain engineering science has received a lot of attention over the last decade, propelling beyond the praise of niche Bitcoin fanatics and into the mainstream conversation of banking experts and investors.
In September 2017, JPMorgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon derided Bitcoin: "Information technology'due south worse than tulip bulbs," he said, referencing the 17th-century Dutch tulip market bubble. "Information technology won't finish well. Someone is going to get killed." Lloyd Blankfein, senior chairman of Goldman Sachs, echoed that idea, saying, "Something that moves twenty% [overnight] does not feel like a currency. Information technology is a vehicle to perpetrate fraud."
Despite the skepticism, the question of whether blockchain and decentralized ledger technology (DLT) will replace or revolutionize elements of the cyberbanking organization remains.
And this very loud and public backlash against cryptocurrencies from banks begs another question: What do banks have to exist afraid of?
The short answer is "a lot."
Blockchain and banking: The office of DLT in financial services
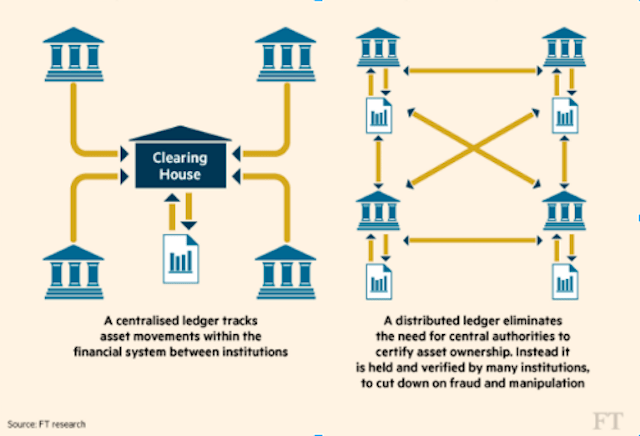
Blockchain technology provides a style for untrusted parties to come to understanding on the state of a database, without using a middleman. By providing a ledger that nobody administers, a blockchain could provide specific financial services — like payments or securitization — without the demand for a bank.
Farther, blockchain allows for the employ of tools like "smart contracts," self-executing contracts based on the blockchain, which could potentially automate manual processes from compliance and claims processing to distributing the contents of a volition.
For use cases that don't demand a loftier degree of decentralization — but could do good from better coordination — blockchain's cousin, "distributed ledger technology (DLT)," could help corporates constitute better governance and standards around data sharing and collaboration.
Blockchain engineering and DLT accept a massive opportunity to disrupt the $5T+ banking manufacture by disintermediating the central services that banks provide, including:
- Payments: By establishing a decentralized ledger for payments (e.yard. Bitcoin), blockchain technology could facilitate faster payments at lower fees than banks.
- Clearance and Settlement Systems: Distributed ledgers tin can reduce operational costs and bring usa closer to existent-time transactions between fiscal institutions.
- Fundraising: Initial Money Offerings (ICOs) are experimenting with a new model of financing that unbundles access to capital from traditional capital-raising services and firms.
- Securities: By tokenizing traditional securities such equally stocks, bonds, and alternative assets — and placing them on public blockchains — blockchain technology could create more efficient, interoperable capital markets.
- Loans and Credit: By removing the need for gatekeepers in the loan and credit industry, blockchain technology can make it more secure to borrow money and provide lower interest rates.
- Trade Finance:By replacing the cumbersome, paper-heavy bills of lading process in the trade finance industry, blockchain technology can create more transparency, security, and trust among trade parties globally.
- Customer KYC and Fraud Prevention: By storing customer data on decentralized blocks, blockchain engineering science can make it easier and safer to share information between financial institutions.
Read on for a deep swoop into how blockchain engineering could turn the traditional cyberbanking manufacture on its head while enabling new business models through applied science. To learn about the other industries blockchain is affecting, take a await at our commodity on 58 industries blockchain could disrupt.
1. Payments
Takeaways
- Blockchain engineering offers a secure and inexpensive way of sending payments that cuts down on the need for verification from third parties and beats processing times for traditional banking company transfers.
- 90% of members of the European Payments Council believe blockchain technology will fundamentally modify the industry by 2025.
Today, trillions of dollars slosh around the earth via an antiquated organization of slow payments and added fees.
If you work in San Francisco and want to ship part of your paycheck back to your family in London, you might have to pay a $25 flat fee for a wire transfer, and additional fees adding up to 7%. Your banking company gets a cut, the receiving bank gets a cut, and you're charged exchange rate fees. Your family unit'south bank might non fifty-fifty register the transaction until a week after.
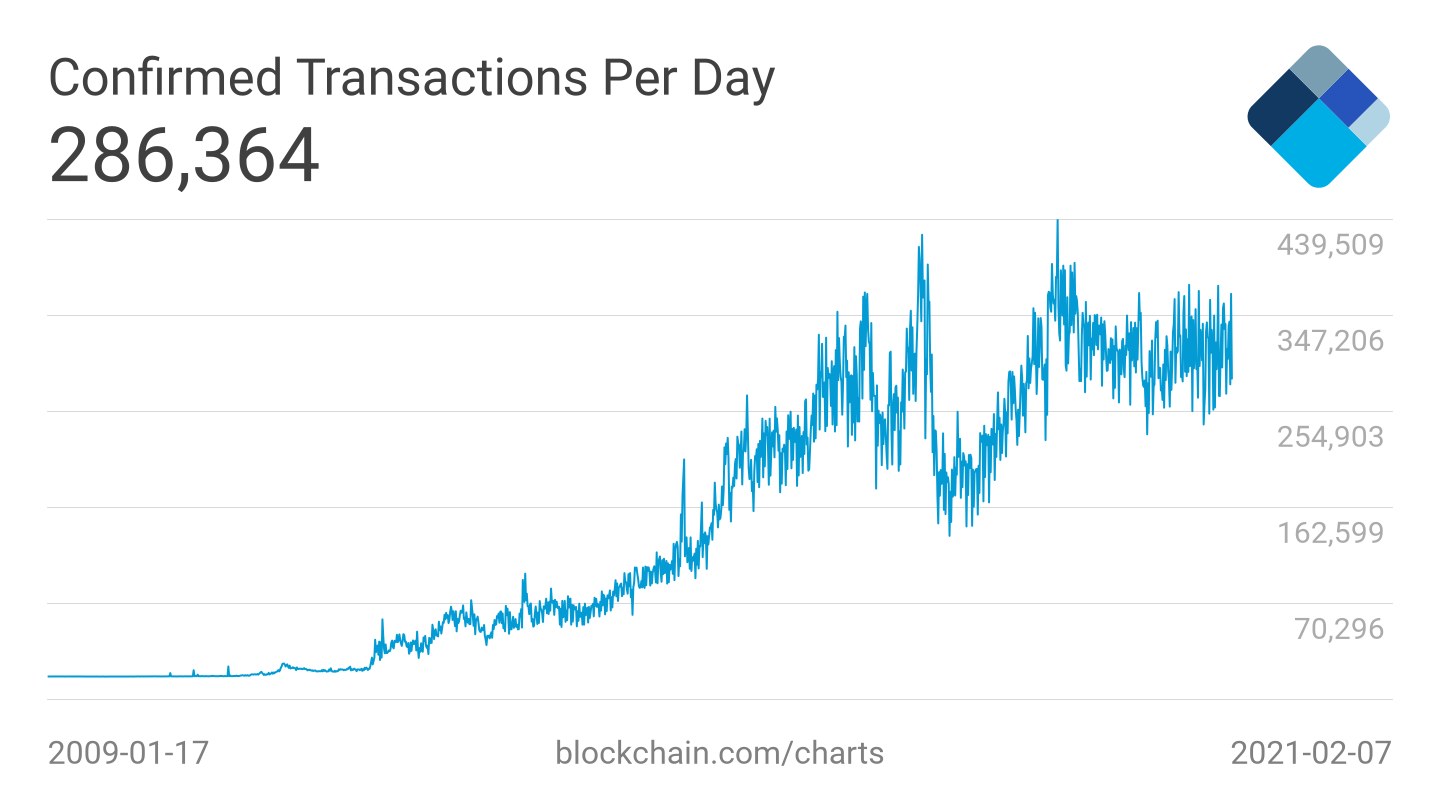
The number of confirmed Bitcoin transactions per day has grown 6x from just over fifty,000 in 2014 to over 300,000 as of February 2021. Source: Blockchain
Facilitating payments is highly profitable for banks, providing them with petty incentive to lower fees. For case, cross-border transactions, from payments to letters of credit, generated $224B in payments revenues in 2019.
Cryptocurrencies similar bitcoin and ether are congenital on public blockchains (Bitcoin and Ethereum, respectively) that anyone can use to send and receive coin. In this way, public blockchains cutting downwards on the need for trusted third parties to verify transactions and give people around the world access to fast, cheap, and borderless payments.
Bitcoin transactions take 10 minutes on average to settle, although this can lengthen to hours or even days in farthermost cases. That's still not perfect, but information technology represents a leg up from the boilerplate 3-day processing fourth dimension for bank transfers. And due to their decentralized and complex nature, crypto-based transactions are hard for governments and regulatory bodies to control, notice, and close down.
Developers are also working on scaling cheaper solutions to process crypto transactions more quickly. Bitcoin Greenbacks and TRON, for example, have relatively depression-priced transactions.
Examples of improved payments through blockchain
While cryptocurrencies are a long way from completely replacing fiat currencies (like the Us dollar) when it comes to payments, the concluding couple of years accept seen mostly upward growth in transaction volume for cryptocurrencies similar bitcoin and ether. In fact, the Ethereum network became the starting time to settle $1T in transactions in i calendar year in 2020.
Some companies are using blockchain applied science to better B2B payments in developing economies. 1 instance is BitPesa, which facilitates blockchain-based payments in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Uganda. The company has processed millions of dollars in transactions, reportedly growing twenty% month-over-month.

Source: BitPesa
BitPesa is as well widely used for remittances sent throughout sub-Saharan Africa, the most expensive region in the world for sending money. Crypto payments platforms such as BitPesa have led to a reduction of over 90% in transfer fees in the region.
Blockchain companies are also focusing on enabling businesses to be able to accept cryptocurrencies every bit payment. For case, BitPay, a payment service provider that helps merchants accept and shop bitcoin payments, has a number of integrations with e-commerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce.
Ethereum-based payments platform Airfox, which was acquired by Brazil-based retailer Via Varejo in May 2020, has partnered with MasterCard to allow customers to pay using its banQi app at global points of sale, besides every bit at every Via Varejo location.
HUPAYX, a South Korea-based crypto payments startup, partnered with several Southward Korean businesses in 2019 to create a payments network. Consumers in the country can at present pay using the HUPAYX mobile app and point-of-sale infrastructure at over 400,000 stores, including duty-free stores and shopping complexes.
Blockchain technology is besides being used to facilitate micropayments, which stand for amounts usually less than a dollar. For instance, SatoshiPay, an online cryptocurrency wallet, allows users to pay tiny amounts to access paid online content on a pay-per-view basis. Users tin load their wallet with bitcoin, US dollars, or whatsoever other payment token supported by the app.
One large reason behind the coming disruption of the payments industry is the fact that the infrastructure supporting it is merely as liable to disruption — the world of clearance and settlements.
2. Clearance and Settlements Systems
Takeaways
- Distributed ledger applied science could let transactions to be settled directly and go on track of transactions improve than existing protocols like SWIFT.
- Ripple and R3, amongst others, are working with traditional banks to bring greater efficiency to the sector.
The fact that an boilerplate bank transfer — every bit described to a higher place — takes iii days to settle has a lot to do with the way our financial infrastructure was congenital.
It's not merely a hurting for the consumer. Moving money around the earth is a logistical nightmare for the banks themselves. Today, a simple bank transfer — from one account to another — has to bypass a complicated system of intermediaries, from correspondent banks to custodial services, before it ever reaches any kind of destination. The two banking concern balances have to be reconciled across a global financial organisation, comprised of a wide network of traders, funds, asset managers, and more.
If you desire to ship money from a UniCredit Banca account in Italy to a Wells Fargo banking concern account in the United states of america, the money transfer volition be executed through the Order for Worldwide Interbank Financial Communication (SWIFT), which sends 37.7M messages a day for more than than 11,000 financial institutions.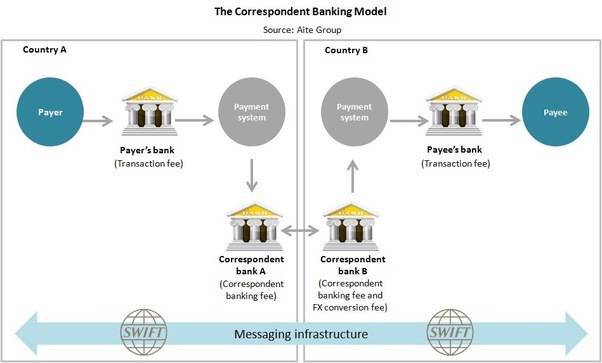
Source: Aite Group
Considering UniCredit Banca and Wells Fargo don't have an established fiscal human relationship, they have to search the SWIFT network for a correspondent banking company that has a relationship with both banks and can settle the transaction — for a fee. Each contributor bank maintains different ledgers, at the originating bank and the receiving bank, which ways that these unlike ledgers have to be reconciled at the finish of the day.
The centralized SWIFT protocol doesn't reallysendthe funds, it but sends the payment orders. The actual money is and then processed through a system of intermediaries. Each intermediary adds additional cost to the transaction and creates a potential point of failure. Further, 60% of B2B payments crave manual intervention, each taking between xv-20 minutes.
Blockchain engineering science, which serves as a decentralized "ledger" of transactions, could disrupt this state of play. Rather than using SWIFT to reconcile each financial establishment'due south ledger, an interbank blockchain could go along track of all transactions publicly and transparently. That ways that instead of having to rely on a network of custodial services and correspondent banks, transactions could be settled straight on a public blockchain.
Further, blockchain technology allows for "atomic" transactions, or transactions that clear and settle as presently as a payment is made. This stands in contrast to current cyberbanking systems, which clear and settle a transaction days after a payment.
That might help alleviate the high costs of maintaining a global network of correspondent banks. An Accenture survey amidst 8 global banks found that blockchain technology could bring down the average cost of clearing and settling transactions by $10B annually.
Examples of improved transactions through blockchain
Ripple, an enterprise blockchain services provider, is the most prominent player working on clearance and settlement. While the company is best known for its associated cryptocurrency XRP, the venture-backed company itself is building out blockchain-based solutions for banks to utilize for clearance and settlement.
SWIFT messages are i-manner, much similar emails, which mean that transactions can't be settled until each party has screened the transaction. By integrating directly with a banking concern's existing databases and ledgers, Ripple'south xCurrent product provides banks with a faster, two-style communication protocol that permits real-time messaging and settlement. Ripple currently has over 300 customers in over 40 countries signed up to experiment with its blockchain network.
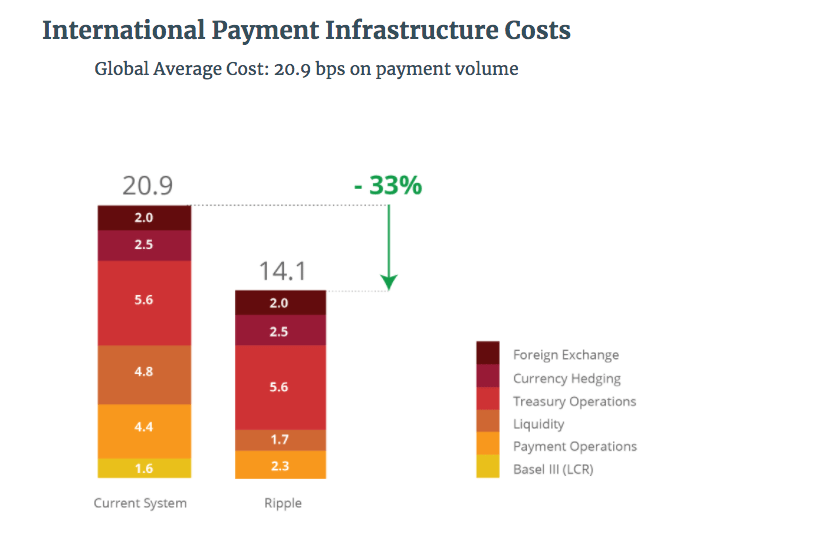
Source: Ripple
Another of Ripple's products, xRapid, is helping settle cross-border transactions in a shorter period. If a trader in United mexican states wants to send money to their analogue in the Usa, a traditional depository financial institution transaction would require that both traders have local currency accounts in the countries they wish to receive their money in. xRapid removes this requirement. The trader in Mexico tin can just use Mexican pesos to buy XRP tokens through the exchange to pay their American counterpart. The US trader can change these XRP tokens for dollars. And this entire transaction can happen in a fraction of a second, Ripple claims.
R3 is some other major player working on distributed ledger technology for banks. It aims to be the "new operating system for financial markets." It raised $107M in May 2017 from a consortium of banks like Banking concern of America Merrill Lynch and HSBC, although information technology has also lost some cardinal members, such as Goldman Sachs, which departed because information technology wanted more than operational control over the organization.
R3'southward technology was used by Switzerland'southward central banking concern for a airplane pilot to settle large transactions between fiscal institutions using digital currencies. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) said in December 2020 that the project, chosen Project Helvetia, was a success. While SNB plans to expand the trial to cross-border payments in 2021, it has not withal decided whether to issue its ain central bank digital currency.
Projects similar Ripple and R3 are working with traditional banks to bring greater efficiency to the sector. They're looking to decentralize systems on a smaller scale than public blockchains by connecting financial institutions to the aforementioned ledger in gild to increment efficiency of transactions.
Blockchain projects are doing more than but making existing processes more efficient, even so. While still in their early on days — and while we continue to see mostly experiments, pilots, and proofs-of-concepts (PoCs) take form — they're creating entirely new types of fiscal activity. The fundraising space is a notable example of this.
3. Fundraising
Takeaways
- In initial coin offerings (ICOs), entrepreneurs raise coin by selling tokens or coins, allowing them to fundraise without a traditional investor or VC firm (and the due diligence that accompanies an investment from one).
- Blockchain company EOS raised over $4B in its year-long ICO ending in 2018.
Raising money through venture capital is an arduous process. Entrepreneurs put together decks, sit through countless meetings with partners, and endure long negotiations over disinterestedness and valuation in the hopes of exchanging some chunk of their company for a check.
In contrast, some companies are raising funds via initial coin offerings (ICOs), powered by public blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
In an ICO, projects sell tokens, or coins, in exchange for funding (often denominated in bitcoin or ether). The value of the token is — at to the lowest degree in theory — tied to the success of the blockchain company. Investing in tokens is a manner for investors to bet straight on usage and value. Through ICOs, blockchain companies tin brusque-circuit the conventional fundraising process by selling tokens directly to the public.
Some high-profile ICOs have raised hundreds of millions — even billions — of dollars before proof of a viable production. Filecoin, a blockchain information storage startup, raised $257M, while EOS, which is edifice a "world figurer," raised over $4B in its yr-long ICO.
Withal, regulators are putting a serious damper on ICOs.
Afterwards soaring in early 2018, ICO funding has since fallen significantly. In fact, ICOs raised just $371M in 2019, down 95% from a year earlier.
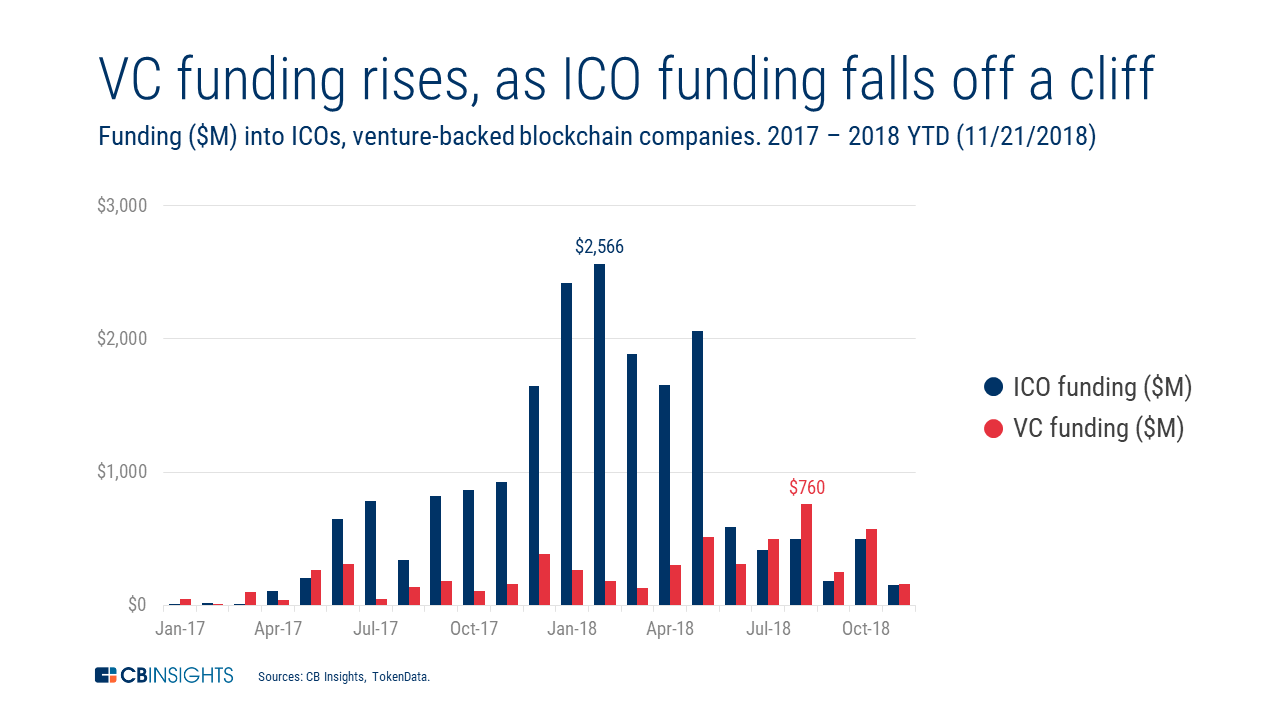
At the aforementioned time, initial money offerings represent a epitome shift in how companies finance evolution.
Start, ICOs occur globally and online, giving companies access to an exponentially larger pool of investors. You're no longer limited to high-net-worth individuals, institutions, and others who are able to show the government that they're credible investors.
2d, ICOs requite companies firsthand admission to liquidity. The moment you sell a token, it'southward priced on a 24-60 minutes global market. Compare that to 10 years for venture-backed startups. As Earn CEO Balaji Srinivasan says, "the ratio between 10 years and 10 minutes to get the choice of liquidity is up to a 500,000x speedup in time." We're already seeing the touch of ICOs on the fundraising market.
Venture uppercase firms have taken notice, with Sequoia, Andreessen Horowitz, and Union Foursquare Ventures, among others, all directly investing in ICOs, every bit well as gaining exposure by investing in cryptocurrency hedge funds.
Venrock partner David Pakman has said, "There'due south no question that crypto will disrupt the business organisation of venture capital letter. And I promise it does. The democratization of everything is what has excited me almost technology from the beginning."
Examples of improved fundraising through blockchain
While the majority of ICOs thus far take been for pre-acquirement blockchain projects, we're seeing more and more engineering companies build around a paradigm of decentralization.
Messaging app Telegram, for instance, raised $1.7B via ICO. The idea behind the ICO is to sell tokens to users and bootstrap a payment platform on top of the messaging network. If, as blockchain advocates predict, the next Facebook, Google, and Amazon are congenital around decentralized protocols and launched via ICO, information technology will eat directly into investment cyberbanking margins.
Several promising blockchain companies have emerged around this space. Companies similar CoinList, which began every bit a collaboration between Protocol Labs and AngelList, are bringing digital assets to the mainstream by helping blockchain companies structure legal and compliant ICOs. CoinList has facilitated nearly $1B in transactions since 2017.
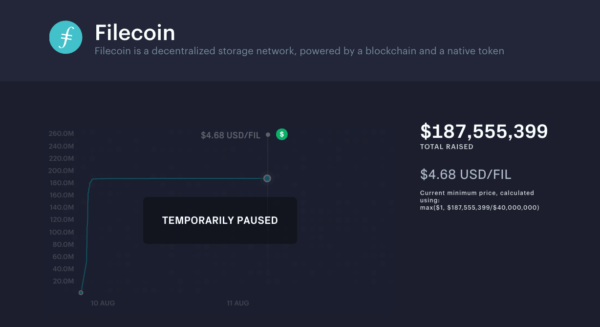
Need for Filecoin'south ICO on CoinList was so loftier that it acquired server overload inside an hr of launch. Filecoin ultimately raised over $257M via ICO.
CoinList has adult a bank-grade compliance process that blockchain companies can access through a streamlined API, helping projects ensure everything from due diligence to investor accreditation. While CoinList's platform is designed for blockchain projects, its focus on reducing the logistical and regulatory load effectually fundraising is being mirrored in the public markets. Investment banks today are experimenting with automation to help eliminate the thousands of work hours that go into an IPO.
And CoinList is just the start. A number of companies are emerging around the new ICO ecosystem, from Waves, a platform for storing, managing, and issuing digital assets, to Republic.co'southward crypto initiative, which is aimed at helping people invest in ICOs for every bit little as $x.
Of course — given regulatory pronouncements — ICO activeness should be taken with a grain of salt, and the bubble of unregulated ICOs largely burst afterward 2018. Even bated from regulatory force per unit area, at that place's no doubt that many of these projects will fail birthday.
What'south interesting is that they're testing out blockchain engineering that could supercede functions of traditional banks. This is not just limited to company fundraising, but also to the underlying material of securities.
Become THE LIST OF BLOCKCHAIN 50 COMPANIES
The Blockchain l is our almanac ranking of the fifty most promising companies within the blockchain ecosystem.
4. Securities
Takeaways
-
-
- Blockchain tech removes the middleman in asset rights transfers, lowering nugget exchange fees, giving admission to wider global markets, and reducing the instability of the traditional securities market place.
- Moving securities on blockchains could save $17B to $24B per year in global trade processing costs.
-
To purchase or sell assets like stocks, debt, and bolt, you need a manner to keep track of who owns what. Financial markets today accomplish this through a complex chain of brokers, exchanges, central security depositories, clearinghouses, and custodian banks. These different parties have been congenital around an outdated system of newspaper ownership that is non just dull, just can exist inaccurate and prone to deception.
Say y'all want to purchase a share of Apple stock. You might place an guild through a stock exchange, which matches you with a seller. In the old days, that meant you'd spend cash in exchange for a certificate of ownership for the share.
This grows a lot more complicated when we're trying to execute this transaction electronically. We don't desire to deal with the mean solar day-to-24-hour interval management of the assets — similar exchanging certificates, bookkeeping, or managing dividends. And so we outsource the shares to custodian banks for safekeeping. Because buyers and sellers don't always rely on the same custodian banks, the custodians themselves demand to rely on a trusted tertiary party to hold onto all the paper certificates.
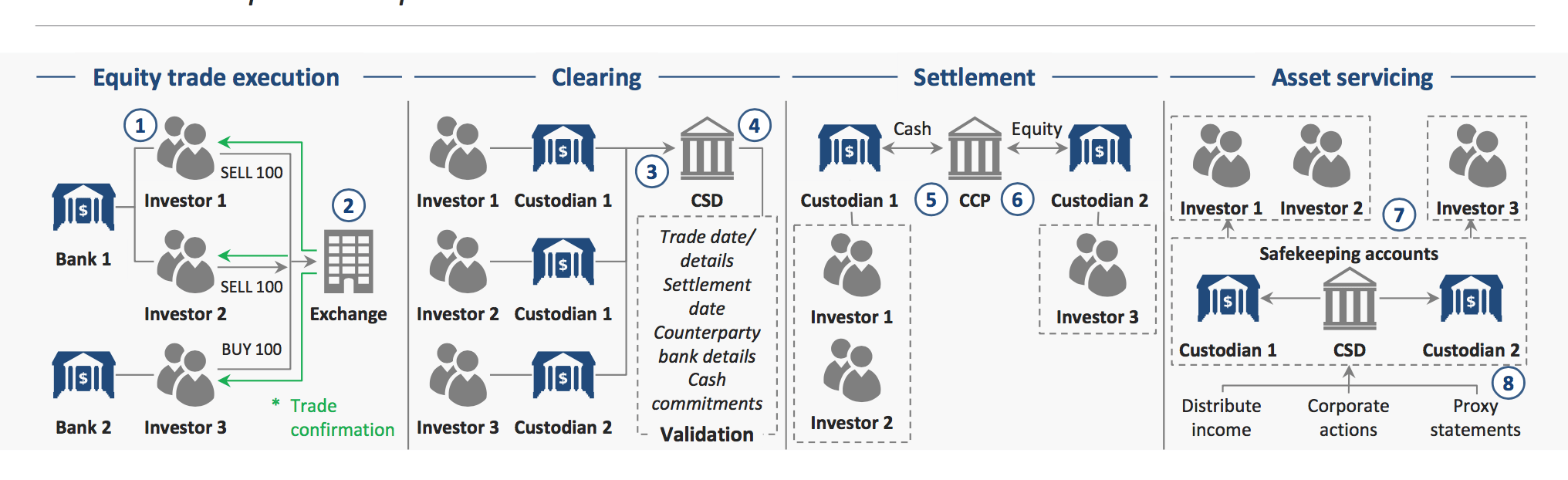
To settle and articulate an order on an exchange involves multiple intermediaries and points of failure.
In do, that means that when you lot buy or sell an asset, that order is relayed through a whole bunch of third parties. Transferring ownership is complicated because each party maintains their own version of the truth in a separate ledger.
Not simply is this system inefficient, but information technology'southward also imprecise. Securities transactions have between 1 to 3 days to settle considering everyone'due south books accept to be updated and reconciled at the end of the solar day. Because there are and then many different parties involved, transactions ofttimes have to be manually validated. Each party charges a fee.
Blockchain technology promises to revolutionize fiscal markets by creating a decentralized database of unique, digital assets. With a distributed ledger, it'due south possible to transfer the rights to an asset through cryptographic tokens, representing assets "off-chain." While Bitcoin and Ethereum have accomplished this with purely digital assets, new blockchain companies are working on ways to tokenize real-world assets, from stocks to real manor to gold.
The potential for disruption is massive. The four largest custody banks in the US — Country Street, BNY Mellon, Citi, and JP Morgan — each oversee over $13T of avails under custody. While fees are typically lower than .02%, profits come up from the sheer book of assets. Using blockchain technology, tokenized securities take the potential to cut out middlemen such as custodian banks altogether, lowering asset commutation fees.
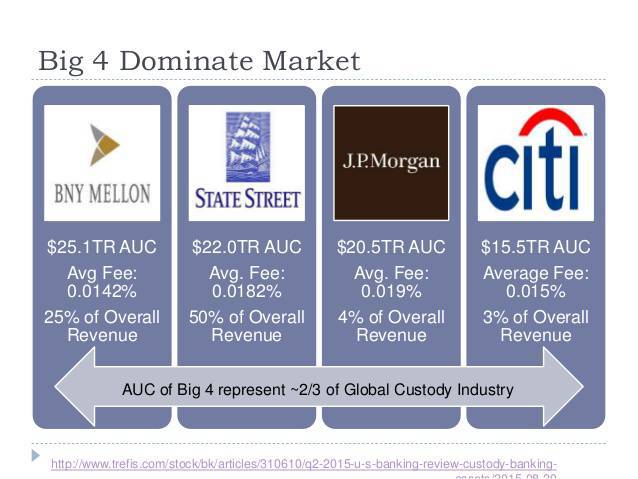
The four largest custodian banks in the U.s.a. each manage $13T+ in avails under custody. Source: Trefis
Farther, through smart contracts, tokenized securities can work as programmable equity — paying out dividends or performing stock buybacks through a couple lines of lawmaking. Finally, putting real-globe avails on blockchain technology has the potential to usher in broader, global access to markets.
Examples of improved securities processes through blockchain
Polymath is one of the blockchain engineering companies that wants to assistance migrate trillions of dollars of financial securities to the blockchain. Polymath is building a marketplace and platform that helps people result security tokens and implement governance mechanisms to help these new tokens meet regulations. So far, Polymath has announced partnerships with Blocktrade, Corl, and Ethereum Majuscule to launch security tokens on the platform.
Meanwhile, financial institutions aren't sitting still. The Australian Stock Exchange plans to replace its system for accounting, clearance, and settlements with a blockchain solution, developed by Digital Asset Holdings, past mid-2022.
Similarly, in 2019, HSBC said information technology plans to digitize the records of $20B worth of assets in custody. The banking concern'southward platform, called Digital Vault, "will digitize newspaper-based records of private placements." This will give investors real-time information about their placements.
In 2017, enterprise-focused blockchain visitor Chain — since caused by Stellar — successfully orchestrated live transactions between the Nasdaq and Citi'south cyberbanking infrastructure via integration. Meanwhile, Overstock'south CEO launched a trading platform chosen tZero, which aims to create a blockchain-backed night pool, or private substitution, for securities that might exist listed on the Nasdaq.
While tokenized assets are a hugely promising use case for blockchain applied science, the biggest hurdle is regulation. It's still unclear if ownership via blockchain technology is legally bounden, while tokens remain an ambiguous term that don't currently have legal standing. Regulatory and legislative guidance will exist key to the success of these nascent projects.
The worlds of the consumer, the financial establishment, and blockchain are slowly converging. Some other space where that convergence has the potential to completely upend the way finance operates today is lending and credit — a domain that's no stranger to disruption.
5. Loans and Credit
Takeaways
-
-
- Blockchain-enabled lending offers a more secure style of offer personal loans to a larger puddle of consumers and would make the loan procedure cheaper, more efficient, and more than secure.
- The start live securities lending took place in 2018 with a $30.5M transaction between Credit Suisse and ING.
-
Traditional banks and lenders underwrite loans based on a arrangement of credit reporting. Blockchain technology opens up the possibility of peer-to-peer (P2P) loans, complex programmed loans that can approximate a mortgage or syndicated loan structure, and a faster and more secure loan process in general.
When you fill out an application for a bank loan, the bank has to evaluate the take chances that you lot won't pay them back. They do this by looking at factors like your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and domicile ownership status. To get this information, they have to admission your credit report provided by one of iii major credit agencies: Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax.
Based on that information, banks price the risk of a default into the fees and involvement collected on loans.
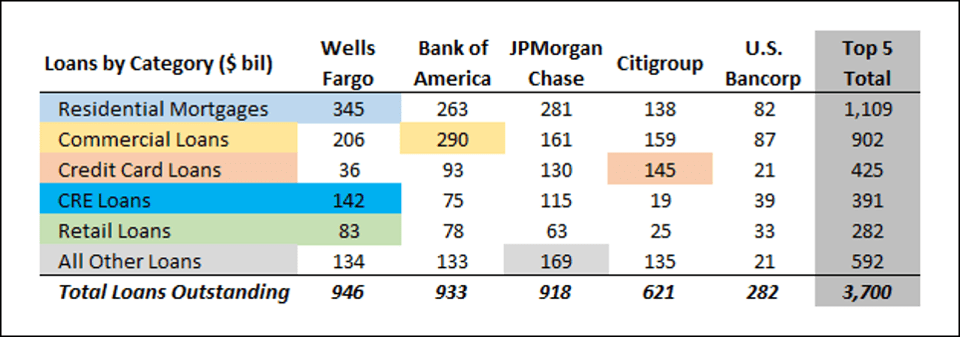
The 5 biggest United states of america banks control $three.7T worth of commercial lending.
This centralized system can be hostile to consumers. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) estimates that 1 in five Americans have a "potentially material error" in their credit score that negatively impacts their power to get a loan. Farther, concentrating this sensitive information within three institutions creates a lot of vulnerability. The September 2017 Equifax hack exposed the credit data of nearly 150M Americans.
Alternative lending using blockchain technology offers a cheaper, more efficient, and more secure style of making personal loans to a broader pool of consumers. With a cryptographically secure, decentralized registry of historical payments, consumers could apply for loans based on a global credit score.
While blockchain projects in the lending space are withal in their infancy, there are a couple of interesting projects out in that location effectually P2P loans, credit, and infrastructure.
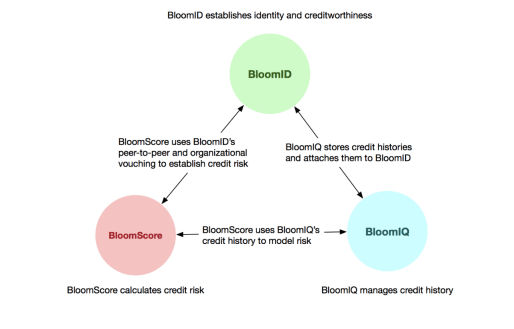
The Bloom protocol seeks to consequence credit based on a track record of successful identity attestation on the network, without trusted third parties. Source: Bloom
Examples of improved lending through blockchain
One company, Common salt Lending, lends greenbacks using a blockchain. Users of SALT Lending'due south platform can borrow coin confronting any bitcoin, ether, or blockchain nugget as collateral. Loans are approved based not on a borrower'southward credit score only on the value of the collateral. To use this platform, a user must purchase the platform's cryptocurrency, SALT. This grants a user membership to be able to take out loans.
Another example of improved lending using blockchain comes from Dharma Labs, a protocol for tokenized debt. Information technology aims to provide developers with the tools and standards necessary for edifice online debt marketplaces.
Meanwhile, Blossom wants to bring credit scoring to the blockchain, and is building a protocol for managing identity, adventure, and credit scoring using blockchain technology.
While virtually of these projects focus on creating liquidity through loans effectually people's existing crypto assets, they're besides jumpstarting the infrastructure that will enable bigger disruption in loans via blockchain.
6. Trade Finance
Takeaways
-
-
- The apply of blockchain and distributed ledger applied science can back up cross-border merchandise transactions that would otherwise be uneconomical because of costs related to trade and documentation processes. It would also shorten delivery times and reduce paper employ.
- With approximately 80-xc% of globe trade relying on merchandise finance, the influence of blockchain on the marketplace would be felt globally throughout all industries that use cross-border trading.
-
Trade finance exists to mitigate risks, extend credit, and ensure that exporters and importers can appoint in international merchandise.
It is a pivotal part of the global financial system, and yet information technology oftentimes operates on blowsy, transmission, and written documentation. Blockchain represents an opportunity to streamline and simplify the circuitous world of merchandise finance, saving importers, exporters, and their financiers billions of dollars every yr.
Blockchain engineering has had an increasingly regular presence in trade programs for a few years now, just its mainstream office in bills of lading and credit has merely recently begun to firm.
Similar many industries, the trade finance market has suffered from logistical setbacks due to former, outdated, and uneconomical manual documentation processes for years. Physical messages of credit, given by one party's banking company to the other party's banking company, are still oftentimes used to ensure that payment volition be received.
Blockchain technology, by enabling companies to securely and digitally prove country of origin, product, and transaction details (and whatsoever other documentation), could help exporters and importers provide each other with more visibility into the shipments moving through their pipelines and more than assurance of delivery.
One of the greatest risks to merchandise parties is the threat of fraud, which is greater because of a lack of confidentiality and footling oversight on the period of goods and documentation. This opens up the possibility of the aforementioned shipment being repeatedly mortgaged, an unfortunate occurrence that happens then oftentimes that commodity trade finance banks write it off as a cost of business.
Through blockchain technology, payments between importers and exporters could take place in tokenized class contingent upon delivery or receipt of appurtenances. Through smart contracts, importers and exporters could gear up rules that would ensure automated payments and cut out the possibility of missed, lapsed, or repeatedly mortgaged shipments.
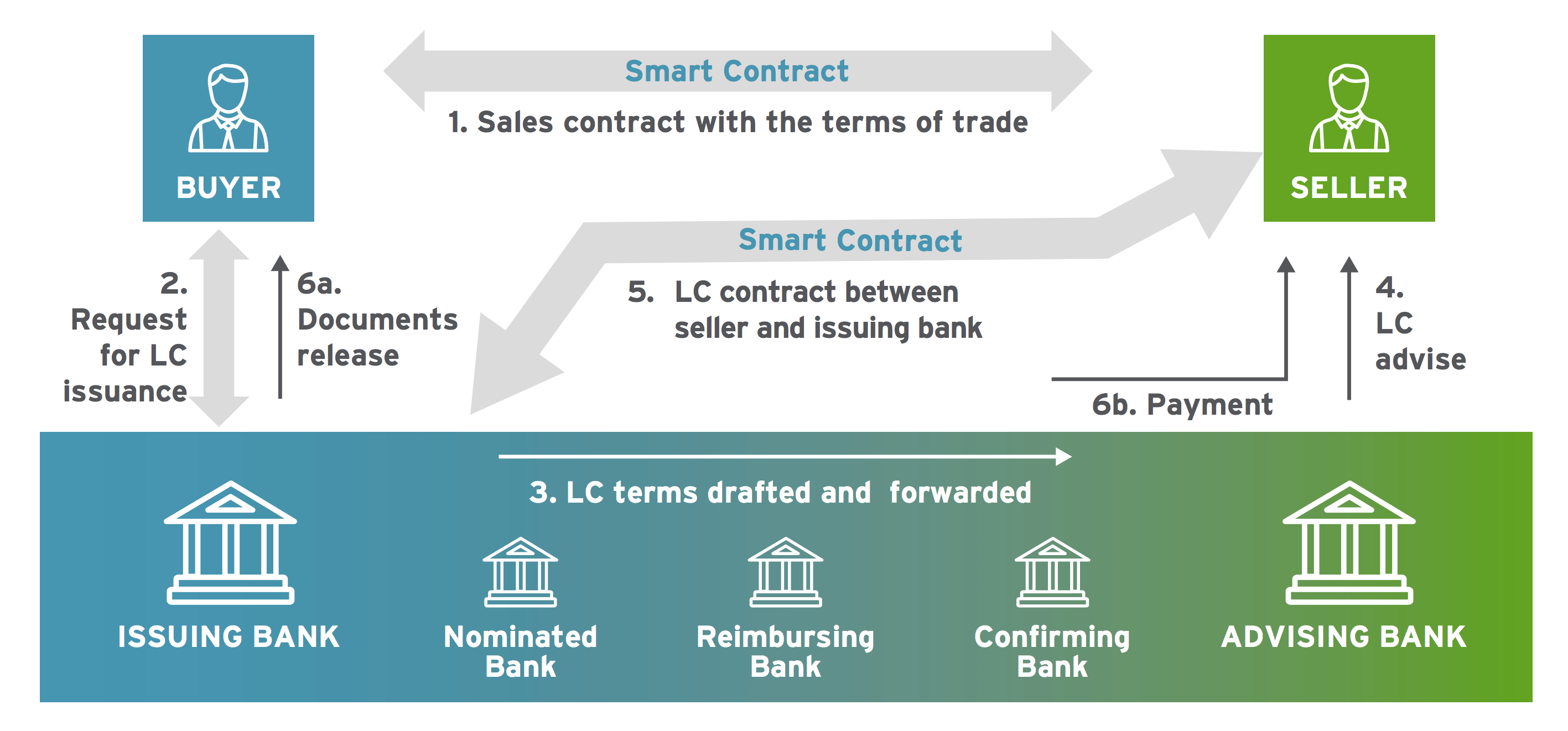
Source: Cognizant
The adoption of blockchain engineering science in trade finance could mean greater trust between merchandise parties, increasing global business concern, while also hiding confidential information such every bit pricing and trade secrets when necessary.
It would also requite buyers improve insight into where their goods originate from and when they've been shipped. Under traditional systems, this information is often incomplete. But a blockchain could enable consumers to be updated at each footstep of the trade, further increasing trust and transparency.
Examples of improved trade financing through blockchain
Arguably, the time has come for blockchain in trade finance, with multiple companies and banks weighing in to find a solution that will stick.
Standard Chartered and HSBC are 2 banks that take joined consortia defended to using blockchain technology to ready trade finance.
One of those consortia is Voltron, run by R3 and CryptoBLK, which operates a blockchain platform for digitizing paper letters of credit.
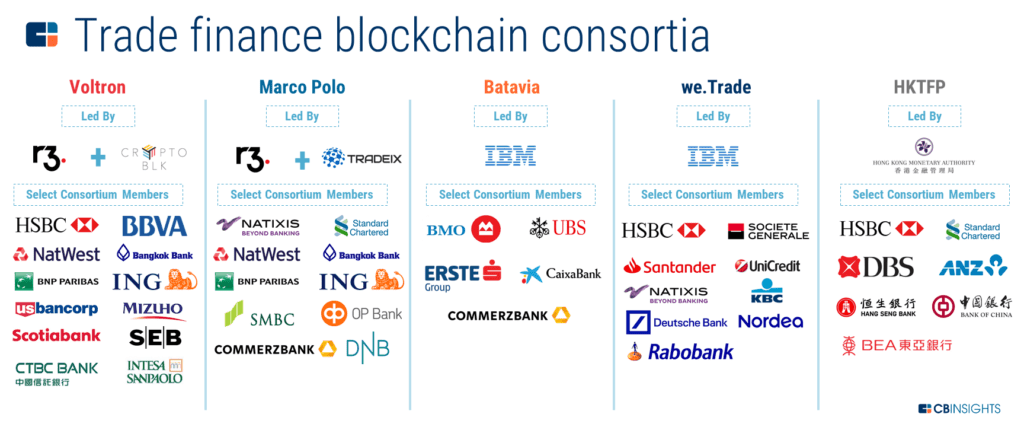
In Oct 2020, DBS and Standard Chartered said that they were working on a blockchain-based merchandise finance platform called Merchandise Finance Registry. The platform is intended to help detect fraud and duplicate financing for a unmarried transaction in existent time. The 2 banks take launched this project in partnership with 12 other banks, including ABN Amro, Deutsche Banking company, ICICI Bank, and Lloyds.
Fintech companies such as Israel-based Wave take developed platforms that enable finance groups to provide letter credit transactions every bit a blockchain solution.
With Wave'south platform, EuroFinance in Barcelona was able to provide a blockchain solution to Ornua and Seychelles Trading Company to streamline their supply chain, reduce transaction costs and documentation errors, and chop-chop transfer documents to customers around the world.
In this instance, the trade process for almost $100,000 of cheese and butter, from the issuing of the letter of credit to the approval of it, took less than 4 hours, drastically down from the traditional time of 7-x days.
Blockchain and DLT accept also enabled trade between Commonwealth of australia and Nippon by facilitating trade-related processes from alphabetic character of credit issuance to the commitment of trade documents. Here, the trade procedure was carried out by Hyperledger Material — built by the Linux Foundation — and secured by IBM.
While all of these projects focus on creating simpler processes to secure merchandise financing, ane other important part of the process for a fiscal institution is completing their due diligence for each customer and transaction. And blockchain engineering has a solution to improve this important step.
7. Customer KYC and Fraud Prevention
Takeaways
- Blockchains can store customer information on unlike blocks, which could help prevent attacks on customer information.
- Blockchain technology for KYC purposes tin bring down costs for the cyberbanking sector past up to $160M annually.
Apart from the day-to-day activities of clearing transactions, processing payments, and trading, a banking concern besides needs to onboard customers, verify their identity, and ensure their information is in order. This procedure is called "know your customer" (KYC).
Banks tin spend up to 3 months executing all KYC proceedings, which include verification of photo IDs, documents such as address proofs, and biometrics. A delayed KYC process may crusade some customers to end their human relationship. According to a Thomson Reuters survey, 12% of companies said that they had inverse their banking company because of delays in the KYC process.
Apart from time and effort, complying with KYC rules also costs banks money. Banks finish up spending upwards to $500M annually on KYC compliance and client due diligence.
Blockchain tech can help reduce the human effort and toll involved in KYC compliance. With KYC customer data stored on a blockchain, the decentralized nature of the platform would permit all institutions that require KYC to admission that data. Using blockchain for KYC purposes could reduce personnel requirements for banks by x%, equating to cost savings of up to $160M annually.
Another security process where blockchain can aid banks is detecting fraud and cyberattacks.
A rise in fraud and cyberattacks is one of the leading causes of concern for the cyberbanking industry, according to BNY Mellon Treasury Services. Since well-nigh banks have centralized ledger systems that store all customer information, it becomes easier for hackers to attack and access that information.
By decentralizing the storage of information, blockchain engineering science helps preclude a hacker from gaining easy access to all information at one time.
Another way of ensuring safe transactions online is by using blockchain-based smart contracts. These contracts operate on an "if/and then" ground, which means that the next step of the process won't happen if the prior one hasn't been completed, allowing for more than failsafes in the process of transacting.
Examples of improved KYC through blockchain
Blockchain-based credit scoring platform Bloom allows customers to create blockchain-based profiles using its mobile application. Bloom'south identity monitoring tool, meanwhile, continually scans the cyberspace and the nighttime web to place whatever potential leaks of a customer's information.
Ripple's xCurrent also stores client details on blocks and passes on important information to different banks. This allows for real-fourth dimension exchange of letters to authenticate customers and transactions, resulting in a quicker settlement of trades.
Similarly, HSBC, Deutsche Bank, and Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Grouping, in partnership with IBM, have tested a service to share KYC information via blockchain. The projection was able to eliminate duplication of effort in collecting the same information by unlike fiscal institutions and digitize and store all customer information securely, among other things.
Beyond the hype of blockchain applied science
Disruption doesn't happen overnight, and much of blockchain technology has yet to be perfected or widely tested.
Die-difficult believers look blockchain and cryptocurrencies to replace banks birthday. Others think that blockchain engineering will supplement traditional financial infrastructure, making it more than efficient.
Information technology remains to be seen to what caste banks embrace the technology. One thing is articulate, notwithstanding: blockchain will indeed transform the industry.
If you aren't already a client, sign up for a gratuitous trial to acquire more than almost our platform.
What Is The Emerging Impact Of Blockchain And Cryptocurrency In The Financial Services Industry?,
Source: https://www.cbinsights.com/research/blockchain-disrupting-banking/
Posted by: hughesmorst1955.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Emerging Impact Of Blockchain And Cryptocurrency In The Financial Services Industry?"
Post a Comment